-
MEANING
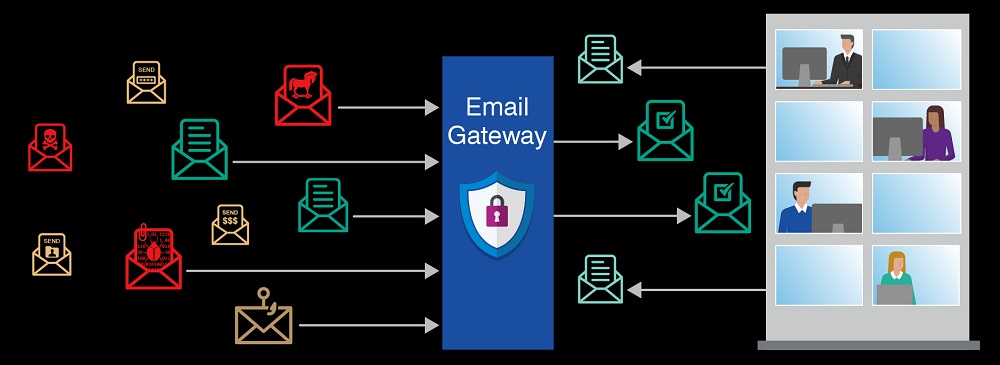
Standing in the way of emails traveling from the public Internet to the company email server is a solution for email security called Secure Email Gateways (SEGs). It can check emails for harmful material in this position before they get to corporate systems. Nevertheless, the SEG’s architecture renders it less appropriate for safeguarding contemporary cloud-based email systems. Check out Email Risk Checker
-
HOW DOES A SECURE EMAIL GATEWAY WORK?
A SEG operates by serving as a stand-in for the email server of a company. When setting up a SEG, the company points its DNS MX record to the cloud-based proxy of the SEG. Emails addressed to the organization will then be routed through the SEG’s proxy.
After that, using threat intelligence, the SEG may filter and examine the email for harmful information. The SEG will transmit the sanitized email to the corporate email server so that the appropriate recipient receives it.
3.MAIN FEATURES
Complete protection against email-borne dangers is what a SEG is meant to offer. Among the essential components of a SEG are:
- Material Disarm and Reconstruction (CDR): CDR breaks down these files, removes harmful material, and reconstructs a sanitized file that may be shared with the user.
- Sandboxing: This material can be evaluated in a setting where harmful code may be run and studied without endangering the organization thanks to sandboxed analysis.
- Data loss prevention, or DLP, is the process of identifying intellectual property (IP) and data that is legally protected in emails and preventing its unapproved use or unsecure transmission.
- Countering Phishing: Phishing is a prevalent cyber threat that may be utilized for data exfiltration, credential theft, and malware distribution.
- Post-Delivery Protection: While examining emails in-line, a SEG could miss some risks, particularly those that are zero-day. To remove a malicious email from the user’s inbox, Post-Delivery Protection leverages email service API integrations.
- DMARC stands for Domain-Based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance. Its purpose is to prevent email spoofing from domains that have enabled it.
-
IMPORTANCE
The biggest danger to business cybersecurity is email-based assaults. One of the most popular ways for cyberattacks to spread malware and get private data is phishing. An attacker may be able to get important information and other internet accounts using a hacked email account.
-
LIMITATIONS
Among the principal drawbacks of SEGs for the contemporary business are:
- Perimeter-Focused Protection: Before sending email traffic to its final destination, many SEGs may route email traffic meant for the corporate email server via a cloud-based proxy for review.
- Single-Layer Security: Some SEGs turn off the security safeguards that email providers (like Google, Microsoft, etc.) automatically give.
- Email Focus: But when businesses switch to alternative cloud-based collaboration and file-sharing solutions, they expose themselves to attack through these unprotected services.
- Bad OPSEC: Change an organization’s DNS MX record to refer to the proxy to enable some SEGs.
- Root Domains: Although Office 365 and G Suite have a root domain whose DNS is controlled by Microsoft or Google, an organization’s DNS MX record may link to its SEG.